云函数云对象
新建云函数
右击cloudfunctions文件夹,点击新建云函数/云对象
例如,新建func云函数,该云函数文件夹下的index.js中,添加代码如下
js
'use strict';
const db = uniCloud.database()
exports.main = async (event, context) => {
return db.collection("article").get()
};
'use strict';
const db = uniCloud.database()
exports.main = async (event, context) => {
return db.collection("article").get()
};
调用云函数
前端页面调用
vue
<template>
<view><button @click="get">请求云函数</button></view>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
get() {
uniCloud
.callFunction({
name: "func1",
})
.then(res => {
console.log(res);
});
},
},
};
</script>
<template>
<view><button @click="get">请求云函数</button></view>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
get() {
uniCloud
.callFunction({
name: "func1",
})
.then(res => {
console.log(res);
});
},
},
};
</script>
调用云函数两种写法
js
// promise方式
uniCloud.callFunction({
name: 'hellocf',
data: { a: 1 }
})
.then(res => {})
// callback方式
uniCloud.callFunction({
name: 'hellocf',
data: { a: 1 },
success(){},
fail(){},
complete(){}
})
// promise方式
uniCloud.callFunction({
name: 'hellocf',
data: { a: 1 }
})
.then(res => {})
// callback方式
uniCloud.callFunction({
name: 'hellocf',
data: { a: 1 },
success(){},
fail(){},
complete(){}
})
云函数传递参数
云函数
js
'use strict';
const db = uniCloud.database()
exports.main = async (event, context) => {
const { limit } = event
return db.collection("article").limit(limit).get()
};
'use strict';
const db = uniCloud.database()
exports.main = async (event, context) => {
const { limit } = event
return db.collection("article").limit(limit).get()
};
前端调用
js
uniCloud.callFunction({
name: 'hellocf',
data: { limit: 1 }
})
.then(res => {})
uniCloud.callFunction({
name: 'hellocf',
data: { limit: 1 }
})
.then(res => {})
新建云对象
示例,新建obj1云对象,该云对象文件夹下的index.obj.js中,添加代码如下
js
const db = uniCloud.database()
module.exports = {
async get() {
return await db.collection("article").get()
}
}
const db = uniCloud.database()
module.exports = {
async get() {
return await db.collection("article").get()
}
}
调用云对象
js
<template>
<view>
<button @click="getObj">请求云对象</button>
</view>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
getObj() {
const obj1 = uniCloud.importObject("obj1");
obj1.get().then(res => {
console.log(res);
});
},
},
};
</script>
<template>
<view>
<button @click="getObj">请求云对象</button>
</view>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
getObj() {
const obj1 = uniCloud.importObject("obj1");
obj1.get().then(res => {
console.log(res);
});
},
},
};
</script>
云对象传递参数
云对象
js
const db = uniCloud.database()
module.exports = {
async get(limit) {
return await db.collection("article").limit(limit).get()
}
}
const db = uniCloud.database()
module.exports = {
async get(limit) {
return await db.collection("article").limit(limit).get()
}
}
前端调用
js
<template>
<view><button @click="getObj">请求云对象</button></view>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
getObj() {
const obj1 = uniCloud.importObject("obj1");
obj1.get(1).then(res => {
console.log(res);
});
},
},
};
</script>
<template>
<view><button @click="getObj">请求云对象</button></view>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
getObj() {
const obj1 = uniCloud.importObject("obj1");
obj1.get(1).then(res => {
console.log(res);
});
},
},
};
</script>
上传云函数/云对象至云端
- 上传单个云函数/云对象:右击该云函数/云对象文件夹,选择
上传部署 - 上传所有云函数/云对象:右击
cloudfunctions文件夹,选择上传所有云函数、公共模块及actions - 请求报错:
云函数在云端不存在,请检查此云函数名称是否正确以及该云函数是否已上传到服务空间,检查第一步或第二步是否成功,在HBuilderX里终端勾选连接云端云函数,重新编译运行
云函数/云对象URL化
- 登录uniCloud后台,选择服务空间
- 左侧菜单栏选择【云函数/云对象】【函数/对象列表】
- 点击需要配置的函数/云对象的【详情】按钮,配置访问路径
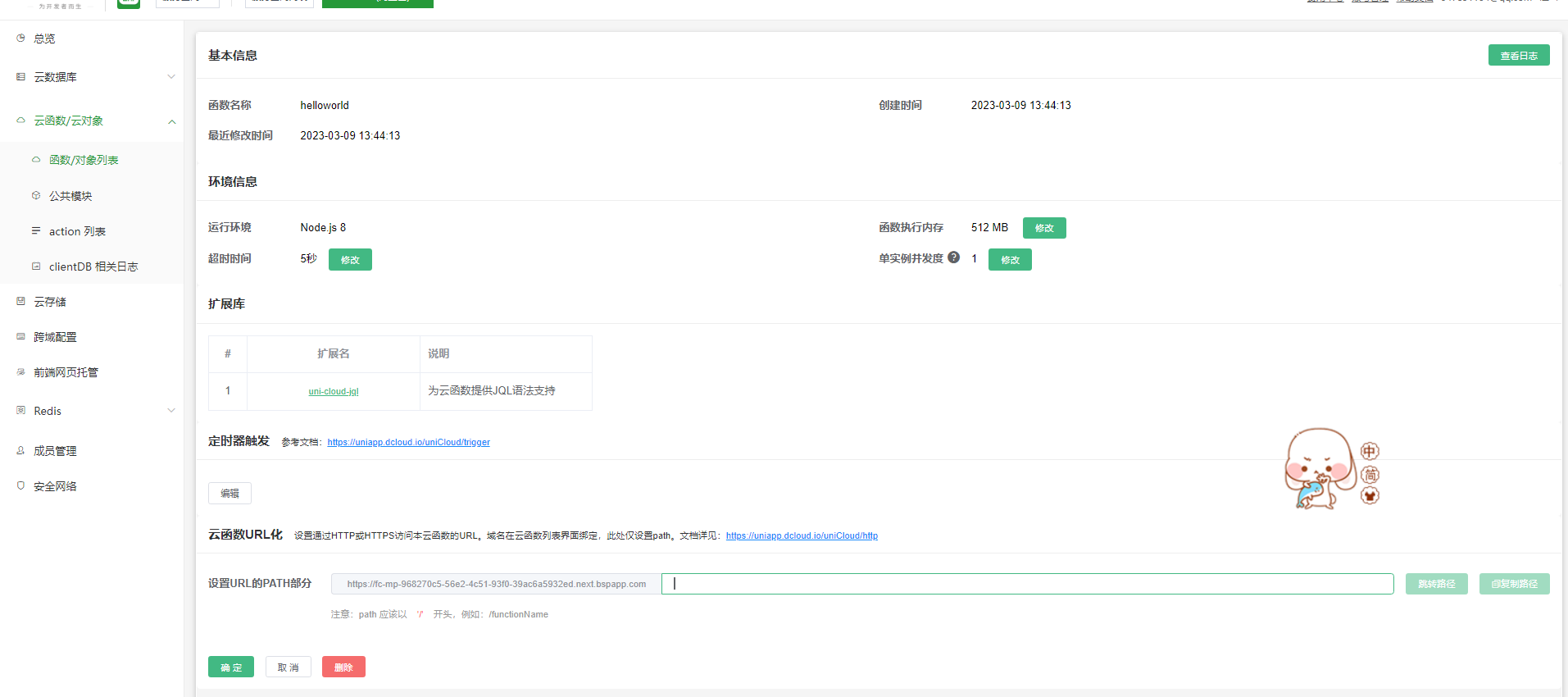
注意
如果配置某云函数路径为/test,实际访问/test、/test/a、/test/b都会执行此云函数,在云函数内可以使用event.path区分访问来源
阿里云使用默认域名时,在浏览器访问url化地址会触发下载。绑定自定义域名则无此问题
云函数请求
URL化,每次修改云函数/云对象代码都需要上传才能更新,并且HBuilderX后控制台不会出现打印信息,这样想调试的话,只能通过返回值的方式,在浏览器查看返回信息
js
'use strict';
const db = uniCloud.database();
exports.main = async (event, context) => {
// return db.collection('article').get();
return { event, context };
};
'use strict';
const db = uniCloud.database();
exports.main = async (event, context) => {
// return db.collection('article').get();
return { event, context };
};
event数据结构如下:
其中get请求传参是queryStringParameters字段,post请求传参是body字段
js
{
path: 'HTTP请求路径,如 /hello',
httpMethod: 'HTTP请求方法,如 GET',
headers: {HTTP请求头},
queryStringParameters: {HTTP请求的Query,键值对形式},
body: 'HTTP请求体',
isBase64Encoded: 'true or false,表示body是否为Base64编码'
}
{
path: 'HTTP请求路径,如 /hello',
httpMethod: 'HTTP请求方法,如 GET',
headers: {HTTP请求头},
queryStringParameters: {HTTP请求的Query,键值对形式},
body: 'HTTP请求体',
isBase64Encoded: 'true or false,表示body是否为Base64编码'
}
示例
使用GET请求https://${云函数Url化域名}/${functionPath}?a=1&b=2,云函数接收到的event为
js
{
path: '/',
httpMethod: 'GET',
headers: {HTTP请求头},
queryStringParameters: {a: "1", b: "2"},
isBase64Encoded: false
}
{
path: '/',
httpMethod: 'GET',
headers: {HTTP请求头},
queryStringParameters: {a: "1", b: "2"},
isBase64Encoded: false
}
使用get请求
js
uni.request({
method: 'POST',
url: 'https://${云函数Url化域名}/${functionPath}',
data: {
a: 1,
b: 2
},
success(res) {
console.log(res);
}
})
// 云函数收到的event为, 注意如果直接return此格式数据可能会被作为集成响应处理,参考下面的集成响应文档
{
path: '/',
httpMethod: 'POST',
headers: {
...
"content-type": 'application/json'
},
isBase64Encoded: false,
body: '{"a":1,"b":2}', // 注意此处可能是base64,需要根据isBase64Encoded判断
uni.request({
method: 'POST',
url: 'https://${云函数Url化域名}/${functionPath}',
data: {
a: 1,
b: 2
},
success(res) {
console.log(res);
}
})
// 云函数收到的event为, 注意如果直接return此格式数据可能会被作为集成响应处理,参考下面的集成响应文档
{
path: '/',
httpMethod: 'POST',
headers: {
...
"content-type": 'application/json'
},
isBase64Encoded: false,
body: '{"a":1,"b":2}', // 注意此处可能是base64,需要根据isBase64Encoded判断